
Causes of mental health problems in young adults have become a growing concern in recent years. Recent reports suggest that mental health issues among children and adolescents are on the rise. However, is this entirely accurate?
Various reasons contribute to mental health problems in children, and it’s essential to understand these factors.
While it’s true that more children are experiencing mental health issues today than in the past, the lack of concrete data makes it challenging to assess the situation accurately. As we develop better ways to recognize and address these issues, more cases are likely to come to light.
Causes of Mental Health Issues in Children:
- Family and parenting style
- Social environment
- Peer pressure
- School environment and academic stress
- Impact of social media
Rather than blaming the child, it’s essential to understand the underlying causes of their behavior and work towards creating a supportive environment. A democratic family atmosphere can foster holistic development and promote mental well-being in children.
The recent Netflix series “Adolescence” highlights the importance of mental health in children and the various factors that contribute to it. The series emphasizes how a child’s behavior and attitudes are shaped by their family, surroundings, school, friends, and social media. Parenting and environment play a significant role in shaping a child’s behavior, attitudes, and mental health. The series also highlights the various pressures children face in today’s social media age, making it essential to prioritize their mental well-being.
Need to Talk to Someone?
Book a private online session with a licensed therapist
By recognizing the importance of mental health in children and working towards creating a supportive environment, we can help them develop into happy and healthy individuals. The report, On Edge: Understanding and Preventing Young Adults’ Mental Health Challenges, is based on a nationally representative survey of young adults (ages 18–25), teens, and parents conducted in December 2022. Thirty-six percent (36%) of young adults who responded to the survey reported anxiety compared to 18% of teens; 29% of young adults reported depression compared to 15% of teens.
Causes of mental illness in young adults
Mental health issues in children can only be understood through a multifaceted approach. A collective effort is necessary to address these issues. Providing a healthy environment during childhood is crucial. Additionally, giving children time for stress-free activities that bring them happiness is essential. This can only be achieved through a collaborative approach.
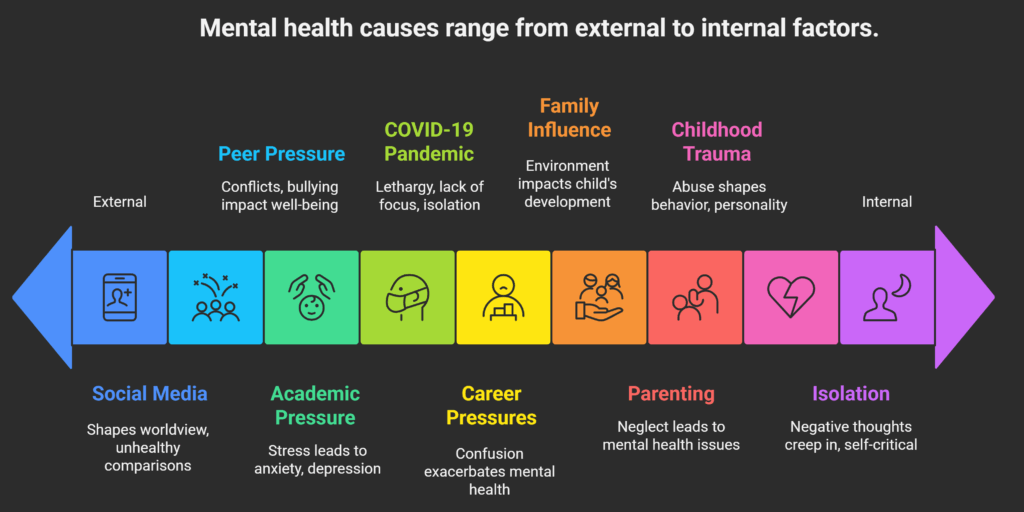
1. Childhood Abuse and Trauma
- Childhood abuse and trauma are significant contributors to mental health issues in children.
- Traumatic experiences during childhood can shape a person’s behavior, personality, and overall well-being.
- Any form of abuse or neglect can lead to long-lasting trauma, affecting a child’s mental health and development.
2. Academic Pressure
- Academic pressure is a significant stressor for children in today’s world. The pressure to perform well academically, fueled by family and societal expectations, can profoundly impact a child’s mental health.
- This stress can lead to anxiety disorders, depression, and even suicidal tendencies.
- The increasing number of children succumbing to academic pressure and resorting to suicidal measures is a concerning trend.
3. Peer Pressure
- During adolescence, children often prioritize their relationships with friends over family members.
- As a result, conflicts and bullying among friends can significantly impact a child’s mental well-being.
- Bullying, ragging, and hurtful jokes can all contribute to mental health issues in children.
4. Influence of Social Media
- In today’s digital age, children are heavily influenced by social media. With technology advancing rapidly, it’s challenging to avoid social media altogether.
- However, excessive phone and social media use can lead to addiction and negatively impact mental health.
- The ideas and concepts children are exposed to on social media can shape their personality and worldview, often in unhealthy ways. Social media’s influence on children’s mental health is a growing concern.
5. Career-related Confusions/Pressures
- Young adulthood is a time when children start thinking about their careers and future. The pressure from society and family can cause significant mental stress for children.
- When children are already confused about their career path, additional pressure from others can exacerbate mental health issues.
6. Influence of Family
- Family plays a significant role in shaping a child’s personality and development.
- Theorists like Jean Piaget and Sigmund Freud emphasize the importance of childhood experiences. A child’s mental health can be significantly impacted by their family environment.
- Factors like unmet basic needs, unhealthy parenting, parental conflict, and substance abuse can negatively affect a child’s development.
- A democratic family environment, where children feel free to express themselves, is essential for promoting mental health.
- In contrast, authoritarian family environments can lead to mental health issues in children, which may become more apparent as they grow older.
- Parenting plays a significant role in shaping a child’s personality.
- According to Albert Bandura’s observational learning theory, children learn by observing their surroundings.
- When children can observe and imitate their parents as role models, it can lead to healthy development. Parents should strive to be positive role models.
- Additionally, Diana Baumrind’s parenting styles underscore the significant role of parenting in shaping a child’s personality.
- Neglectful parenting, in particular, can lead to significant mental health issues in children. Therefore, parents have a substantial impact on their child’s mental health.
8. Isolation and Lack of Social Support
- When children feel isolated, negative thoughts can creep in, leading to various mental health issues.
- Children may become self-critical and develop unhealthy tendencies. Instead of punishing or isolating children who make mistakes, it’s essential to understand and guide them.
- Lack of social support can also contribute to mental health issues in children.
Feeling Overwhelmed?
You’re Not Alone. Get Support from an
Oppam Therapist Wherever You Are
Oppam Therapist Wherever You Are
9. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
- Studies have shown that the COVID-19 pandemic has led to changes in children’s behavior. Teachers have reported increased lethargy, lack of focus, and memory issues in children.
- Parents have also observed increased stubbornness and a lack of focus in their children post-pandemic.
- The pandemic has created a new normal, and it’s essential to find ways to cope with the negative effects.
- Excessive screen time, lack of physical activity, and social isolation have contributed to various mental health issues in children, including addiction.
Causes of Mental Health Problems in Young Adults: Key Triggers in Youth
Unfortunately, the mental health field often faces misconceptions. When children exhibit problems, many people resort to scolding or advising them at home instead of consulting a mental health professional. Instead, when children show behavioral changes, consulting a psychologist or mental health expert can lead to significant improvements. Early intervention can promise a healthier future for children.
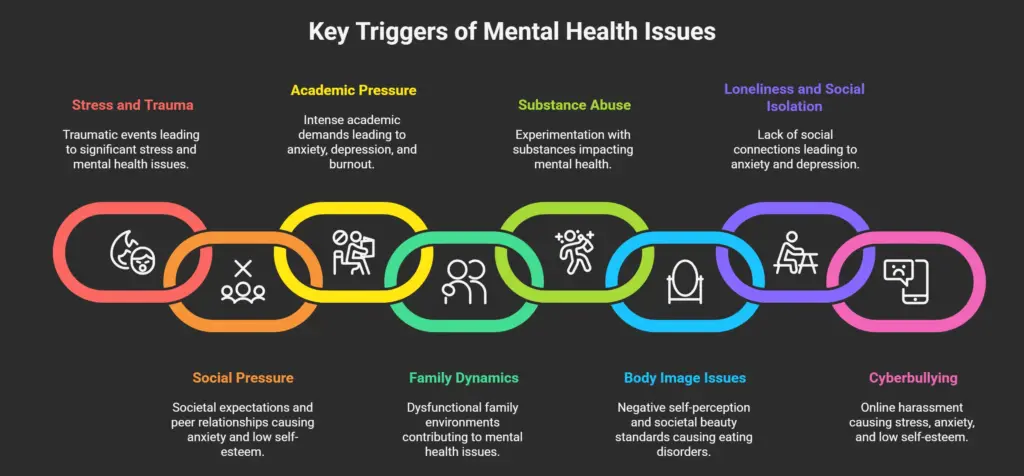
1. Stress and Trauma
Experiencing traumatic events such as abuse, neglect, bullying, or loss of loved ones can be overwhelming for some individuals. These traumatic events can create significant stress and gradually lead to mental health issues.
2. Social Pressure
In today’s era, children face various forms of social pressure. The prevalence of social media and its content has led to increased exposure to such pressures. Additionally, peer relationships, societal expectations, and the stress of conforming to these expectations can all contribute to a significant amount of pressure. This can lead to a decline in self-esteem and contribute to anxiety disorders.
Academic pressure has always been a significant concern for children. However, in today’s era, the pressure created by parents, teachers, and society has become a major issue. Many cases of suicidal attempts and suicides among children can be attributed to academic pressure. The intense academic pressure, competitive mindset, and the stress to perform well can lead to anxiety, depression, burnout, and other mental health issues.
4. Family Dynamics
Family plays a crucial role in shaping a child’s personality and development. A healthy family environment and parenting style can have a profound impact on a child’s behavior and mental health.
On the other hand, dysfunctional family environments, domestic violence, child abuse, parental conflicts, neglect, and toxic parenting can all contribute to the development of mental health issues in children. These factors can have long-lasting effects on a child’s emotional well-being and mental health.
5. Substance Abuse
This era is marked by the availability and temptation of various substances. Peer pressure and the stress of adolescence can lead to experimentation with these substances. Substance abuse can severely impact mental health, leading to various mental health issues.
Numerous studies have demonstrated the detrimental effects of substance abuse on mental health.
6. Body Image Issues
Young adulthood is a period of heightened self-awareness and comparison. Societal beauty standards and comparisons on social media can foster negative self-perception. This can gradually lead to body dissatisfaction, eating disorders, and other issues. Many individuals resort to extreme measures, such as purging or restrictive eating, to maintain an ideal body image. These behaviors can be seen in various forms of media, highlighting the prevalence of eating disorders and body image issues.
7. Loneliness and Social Isolation
Due to a lack of social connections, children may experience feelings of loneliness in various situations. Moreover, this age group is prone to forming cliques and engaging in subtle forms of exclusion, which can lead to social exclusion. This can gradually lead to social isolation, negatively impacting mental health and potentially causing anxiety or depression.
8. Cyberbullying
Cyberbullying is a prevalent issue that children are likely to face in today’s digital age. With the widespread use of phones and gadgets, children are increasingly active online, sharing their lives on social media, and are vulnerable to online harassment and bullying. Cyberbullying can cause significant stress, anxiety, and depression, and can erode self-esteem. Children who experience cyberbullying may become withdrawn, fearful, and struggle to interact with others, living in their world. A sense of fear may constantly haunt them.In addition, the inability to cope with problems, lack of assertiveness (saying no to unwanted things), and reduced social support can all contribute to mental health issues in children. At this age, children need supportive relationships and social connections. When these needs are not met, and they feel excluded from groups, they can gradually become socially isolated. This isolation can harm their mental health.
Psychological causes of mental disorders

Various psychological factors can lead children to mental health issues. Mental health plays a significant role in children’s development. Factors such as childhood trauma, stress, negative thought patterns, emotional regulation issues, attachment problems, distorted self-perception, coping mechanism issues, and social learning problems (e.g., observing and imitating negative role models) can all contribute to mental health issues in children. These factors can have a profound impact on a child’s thoughts, personality, and behavior.
Experiencing traumatic events, such as abuse, neglect, or violence, can lead to anxiety, depression, PTSD, and other mental health issues.
2. Stress:
Chronic stress can contribute to anxiety, depression, and burnout by disrupting the body’s physiological response and impacting coping mechanisms.
3. Negative Thought Patterns:
Distorted or negative thinking patterns, such as catastrophizing, rumination, or self-criticism, can contribute to anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem.
4. Emotional Regulation:
Difficulty managing emotions, such as anger, sadness, or fear, can lead to mood disorders, anxiety, and impulsive behaviors.
5. Attachment Issues:
Insecure attachment styles, such as anxious or avoidant attachment, can impact relationships and contribute to mental health issues.
6. Self-Concept:
Negative self-perception, low self-esteem, and body dissatisfaction can contribute to depression, anxiety, and eating disorders.
7. Coping Mechanisms:
Maladaptive coping strategies, such as substance abuse, avoidance, or self-harm, can exacerbate mental health problems.
8. Learned Helplessness:
Feeling powerless or helpless in the face of challenges can contribute to depression, anxiety, and decreased motivation.
9. Social Learning:
Observing and imitating maladaptive behaviors or thought patterns can contribute to mental health issues.
10. Cognitive Biases:
Biases in thinking, such as confirmation bias or negativity bias, can impact perception, judgment, and decision-making.
Children may experience negative events and situations that can cause emotional pain and affect their ability to cope with problems. Trauma can occur when children are physically, emotionally, or sexually harmed, or neglected and ignored. These experiences can have a profound impact on their mental state, personality development, social well-being, and mental health.
Types of Abuse
There are four main types of abuse that children may experience:
- Physical Abuse: Physical harm, injury, or cruelty that can cause physical and emotional distress.
- Emotional Abuse: Manipulating a child’s emotions, imposing emotional burdens, and causing emotional distress.
- Sexual Abuse: Using children for sexual purposes, including child pornography, which can cause significant trauma.
- Neglect and Emotional Neglect: Ignoring a child’s needs, rejecting them, and blaming them, which can also lead to trauma.
Childhood Trauma and Development
Psychologists like Erik Erikson, Carl Jung, and Sigmund Freud emphasize the importance of early childhood years in development. Erikson highlights the role of social experiences and relationships in shaping a child’s personality. Attachment to primary caregivers is crucial, and neglect can lead to trust issues.
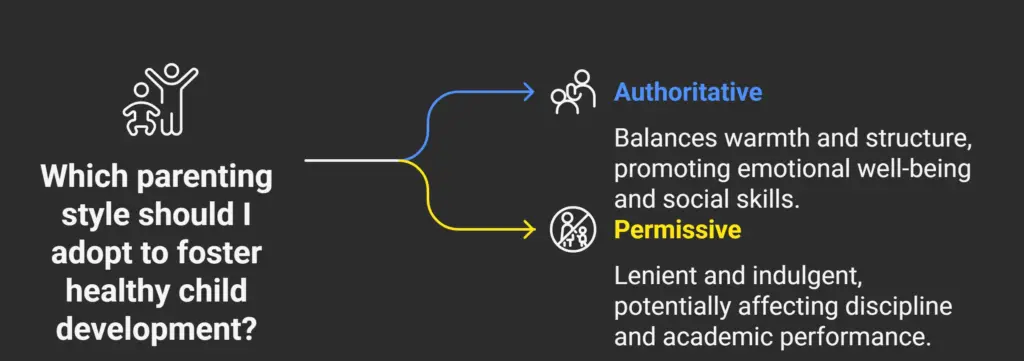
1.Parenting Styles
Parenting styles significantly impact a child’s development. There are four main types:
- Permissive Parenting: Lenient and indulgent, often avoiding conflicts.
- Authoritative Parenting: Balanced approach, setting clear boundaries while being supportive.
- Neglectful Parenting: Ignoring a child’s needs and showing little interest.
- Authoritarian Parenting: Strict and controlling, often using punishment.
2.Family and School Environment
A supportive family environment is vital for a child’s development. Toxic parenting can lead to behavioral issues and mental health problems. Schools can also be a source of stress, with bullying, body shaming, and pressure to perform academically.
3.Consequences of Trauma
Unresolved trauma can lead to depression, anxiety, and suicidal tendencies. Children who experience trauma may become aggressive or develop substance abuse issues. Parents, educators, and society need to provide a supportive environment to help children overcome challenges and develop healthy relationships.
Impact of Trauma on Children
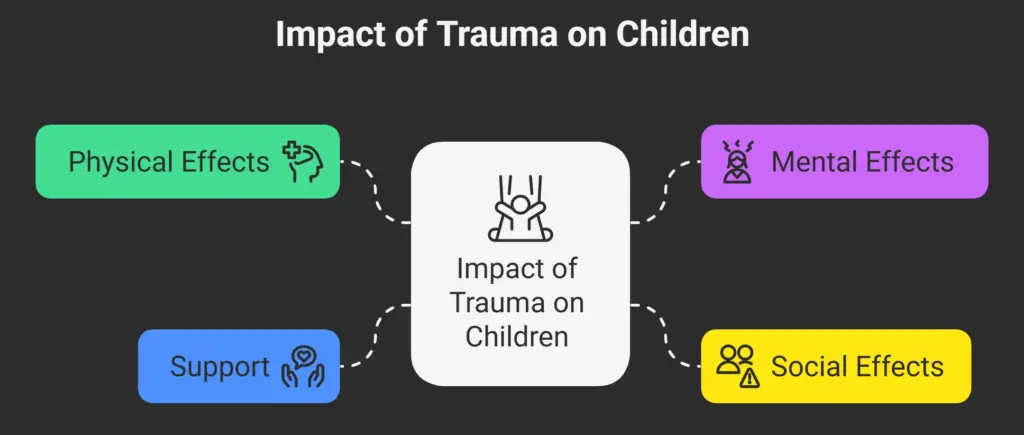
Physical, mental, and social problems faced by children create significant stress, affecting their growth and development. Chronic stress can weaken their immune system, slow down central nervous system development, and impair brain function.
Children experiencing trauma may exhibit fatigue, insomnia, loss of appetite, or increased appetite. They may develop post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), characterized by recurring memories of the traumatic event.
1.Long-term Consequences
Untreated trauma can lead to antisocial behavior, aggression, and substance abuse. Children may develop emotional dysregulation, struggling to manage their emotions. Trauma can also cause social phobia, anxiety disorders, and depression.
2.Effects of Childhood Trauma on Adulthood
Adults who experienced trauma in childhood may struggle with relationships, trust issues, and self-esteem. They may exhibit attention-seeking behavior, aggression, or avoidance of responsibilities.
3.Importance of Support
Parents, caregivers, and society need to provide support and understanding to children who have experienced trauma. Media sensationalism can exacerbate the trauma, highlighting the need for responsible reporting.
Feeling Overwhelmed?
You’re Not Alone. Get Support from an
Oppam Therapist Wherever You Are
Oppam Therapist Wherever You Are
Trauma has long-term effects on mental health, relationships, and social well-being. Providing a supportive environment and addressing trauma can help mitigate its impact and promote healthy development.
Depression is a complex and multifaceted mental health disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest or pleasure in activities. It can affect anyone, regardless of age, background, or circumstances.
Depression among children has increased significantly due to various reasons. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 300 million people worldwide are affected by depression. According to WHO, Depression is the fourth leading cause of disability worldwide and is expected to become the second leading cause of disability by 2030, surpassed only by heart disease
I recall reading a news article in The Times of India, citing recent studies that indicate a growing prevalence of depression among young people in India. The studies suggest that the prevalence rate ranges from 31% to 57%. According to the report, UNICEF’s findings also indicate that one in seven young people aged 15-24 in India experience depression, often exhibiting a lack of interest in activities.
Need to Talk to Someone?
Book a private online session with a licensed therapist
India and the world are facing a significant and growing mental health crisis. However, it’s worth noting that effective scientific treatments, counseling, and therapies are available for depression. A positive approach, free from stigma and misconceptions about mental health and depression, is essential. Depression is a leading cause of suicide. By adopting a supportive and positive approach, we can work towards preventing suicides and addressing depression to some extent.
Let’s look into the reasons:
Academic-Related Factors:
- Pressure to Perform: Excessive academic expectations, competition, and pressure to achieve high grades can lead to stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Overload and Burnout: Managing heavy coursework, extracurricular activities, and part-time jobs can lead to physical, emotional, and mental exhaustion.
- Fear of Failure: Fear of not meeting expectations, failing exams, or not being good enough can contribute to anxiety and depression.
- Transition Challenges: Adjusting to new academic environments, such as transitioning from high school to college or university, can be stressful and overwhelming
Social and Emotional Factors:
- Social Isolation: Feeling disconnected from peers, family, or friends can contribute to feelings of loneliness and depression.
- Bullying and Harassment: Experiencing bullying, harassment, or discrimination can lead to anxiety, depression, and trauma.
- Relationship Issues: Difficulties with romantic partners, friends, or family members can contribute to emotional distress and depression.
- Self-Esteem and Body Image: Negative self-perception, body dissatisfaction, and low self-esteem can contribute to depression.
Personal and Environmental Factors:
- Family History: A family history of depression or other mental health conditions can increase the risk of developing depression.
- Trauma and Adversity: Experiencing traumatic events, such as abuse, neglect, or loss of a loved one, can contribute to depression.
- Sleep Deprivation: Chronic sleep deprivation can contribute to mood disorders, including depression.
- Substance Abuse: Experimentation with substances can exacerbate existing mental health conditions or lead to new challenges.
In today’s context, it’s crucial to consider the role of excessive phone use and digital addiction in contributing to mental health issues. These factors have become significant contributors to mental problems in children. The phenomenon of “brain rot” is a concerning outcome of excessive phone use. It’s essential to discuss digital addiction and its associated mental health issues to address this growing concern.
Understanding Brain Rot
“Brain rot” refers to the mental and cognitive decline resulting from excessive exposure to low-quality online content, such as videos. Recent studies have shown that consuming such content can lead to various mental health issues and cognitive impairment.
Although “brain rot” is not a formally recognized medical condition, its consequences can be significant.
The Consequences of Excessive Screen Time
Excessive screen time and consumption of negative, low-quality content can lead to “brain rot.” This phenomenon significantly impairs problem-solving and decision-making skills. Additionally, it can weaken memory and recall abilities, making it challenging to focus and maintain academic performance. Brain rot is also characterized by decreased attention span and lower academic achievement.
Factors Contributing to Brain Rot
- Constant online availability: Continuous exposure to online content can lead to brain rot.
- Binge-watching: Watching videos for extended periods can contribute to brain rot.
- Excessive social media use: Spending too much time on social media can also lead to brain rot.
Brain Rot Behaviors
- Brain rot behaviors manifest in various forms, including video gaming, which can lead to significant time wastage.
- While some gaming can be considered entertainment, others can lead to gaming disorders.
- The recent controversy surrounding games like Blue Whale and PUBG, which were banned, has given rise to new versions and clones. Currently, games like Free Fire are popular.
- Some children have become so addicted to gaming that they have become aggressive and violent, even harming their family members when denied access to phones.
- Many people have lost money and even their lives due to gaming addiction.
- These games often involve killing virtual characters to earn scores and rewards, which can desensitize players to violence and reduce empathy.
The potential risks of such games include:
- Increased aggression and violence
- Decreased empathy and mutual respect
- Addiction and loss of productivity
- Negative impact on mental health and well-being
It’s essential to recognize the potential consequences of excessive gaming and take steps to mitigate its effects. Parents, caregivers, and society as a whole must be aware of the risks associated with gaming and promote healthy gaming habits and digital literacy.
Zombie Scrolling
- Zombie scrolling refers to the mindless scrolling through content on our phones without any purpose or benefit.
- This behavior can become a habit, leading to a waste of time and a lack of productivity. By engaging in zombie scrolling, we miss out on opportunities to nurture our cognitive abilities.
- Eg, Watching Instagram Reels excessively, scrolling through Instagram without any specific goal
Doom Scrolling
- Doom scrolling refers to the act of continuously searching for and consuming negative and disturbing news and content.
- Individuals engaging in doom scrolling prioritize staying updated with the latest news, regardless of how distressing it may be.
- This behavior is characterized by a fascination with negative news, which can have detrimental effects on mental health.
- Research suggests that doom scrolling can disrupt the brain’s reward system, leading to a preference for negative news over positive ones.
- This can have adverse effects on mental health, including increased stress, anxiety, and decreased well-being.
- By prioritizing negative content, individuals may inadvertently compromise their mental health and overall quality of life.
Social Media Addiction
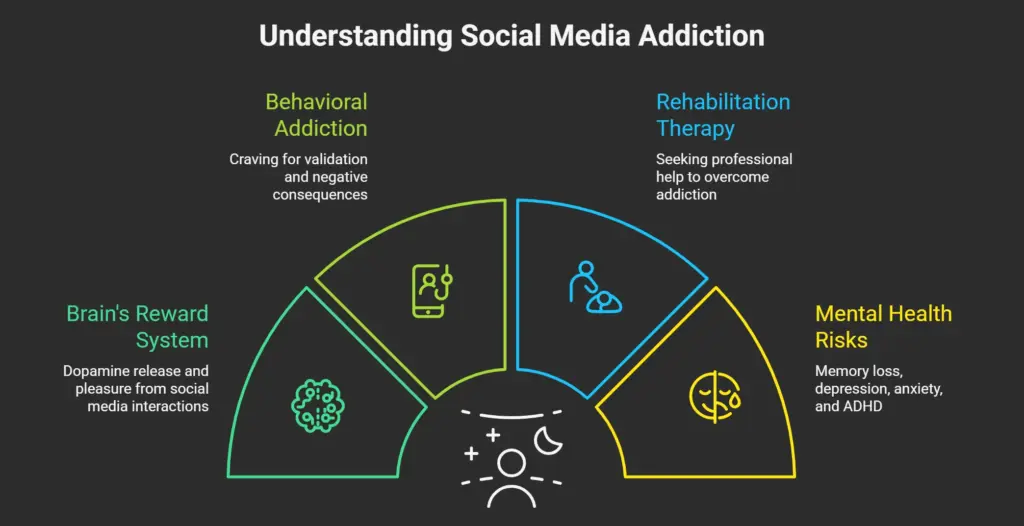
Social media addiction can lead to brain rot, similar to substance abuse. Social media activates the brain’s reward system, releasing dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with happiness and satisfaction. When we share content on social media and receive likes and comments, our brain’s reward centers are stimulated, releasing dopamine and creating a feeling of pleasure. The ventral tegmental area, responsible for reward processing, facilitates dopamine production, leading to feelings of happiness and satisfaction. This can create a cycle of craving for more social media interaction, as our brains become accustomed to the constant stream of validation.
- As our happiness and satisfaction become increasingly tied to social media, we may develop behavioral addiction, despite being aware of the negative consequences.
- Recognizing the potential for addiction and seeking rehabilitation therapy and counseling can help individuals overcome social media addiction and regain control over their behavior.
- It’s essential to acknowledge that addiction can be a complex issue, and overcoming it often requires professional help.
- By understanding the mechanisms behind social media addiction and seeking appropriate support, individuals can work towards developing healthier relationships with social media and improving their overall well-being.
- A study published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health by Peng Shao and Schayu Dong found that TikTok use disorder in high school students can lead to memory loss, depression, anxiety and Stress
- Although TikTok is currently not available in India, similar platforms like Instagram Reels, Facebook Reels, and other video-sharing apps may have similar effects on mental health. The study’s findings highlight the potential risks associated with excessive social media use, particularly among young people.
- A study conducted by Jason Nagata and colleagues investigated the relationship between screen time and behavioral problems in children.
- The study, which included 9,538 adolescents, found that excessive screen time was associated with symptoms of various mental health disorders, including Depression, Conduct Disorder, Somatic Disorder, and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- The study revealed that video chatting, messaging, and video gaming were significant predictors of depression in adolescents.
- These findings highlight the potential risks of excessive screen time on mental health and suggest that parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals should be aware of the potential consequences of prolonged screen time in children.
If you or someone you care about is struggling with mental health challenges, know that you’re not alone. Our experienced therapists at OPPAM are here to support you every step of the way. Facing academic stress, emotional pressure, or digital burnout? OPPAM’s expert therapists can help young adults build resilience, improve well-being, and reclaim their mental health.
Be willing to consult a mental health professional. Make your child’s mental well-being a priority!
Struggling?
Talk to an Oppam Therapist
Get the Support You Deserve Online & Confidential

